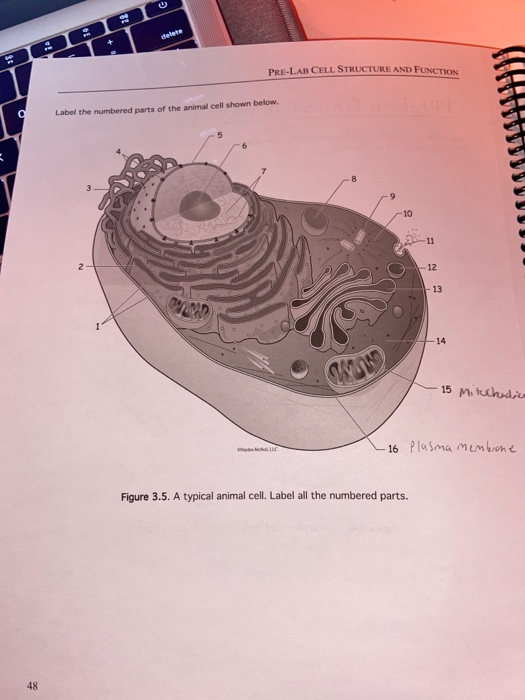
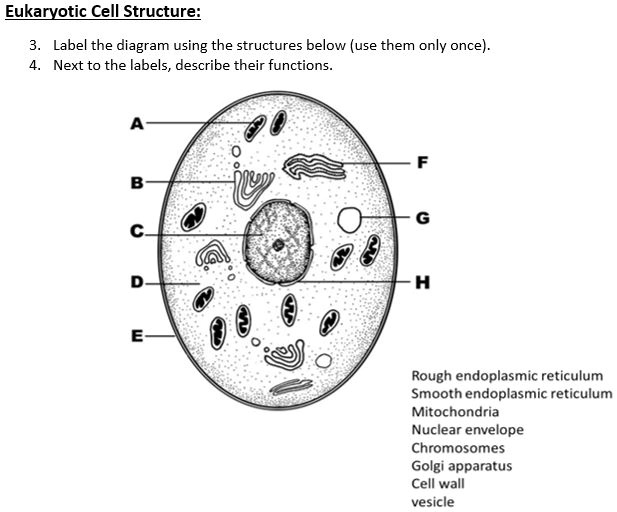
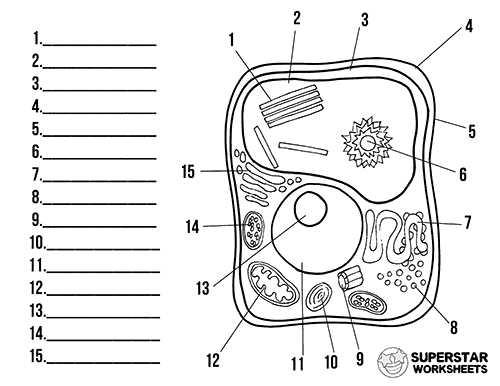
45 cell structure with labels
Capillaries: Anatomy, Function, and Significance - Verywell Health Capillary Structure . Capillaries are very thin, approximately 5 micrometers in diameter and composed of only two layers of cells. The inner layer is made up of endothelial cells with an outer layer of epithelial cells. They are so small that red blood cells need to flow through them single file. Microscopy technique reveals hidden nanostructures in cells and tissues ... Prof. Edward Boyden has developed a new imaging technique called expansion-revealing microscopy that can reveal tiny protein structures in tissues, reports The Economist.. "Already his team at MIT has used it to reveal detail in synapses, the nanometer-sized junctions between nerve cells, and also to shed light on the mechanisms at play in Alzheimer's disease, revealing occasional spirals ...
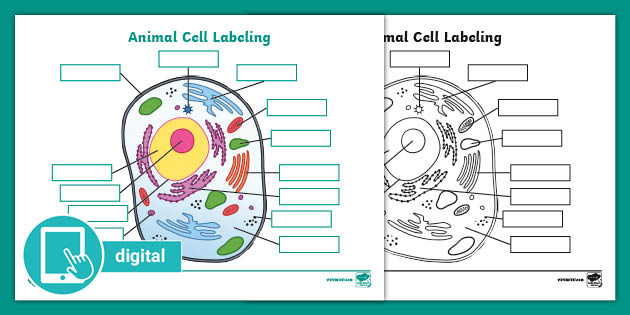
Eukaryotic Cells Quiz - ProProfs Quiz Questions and Answers 1. What are the different parts inside a cell called? A. Organelles B. Bases C. Nucleotides D. Pieces E. Atoms 2. What type of cell is it? A. Bacteria Cell B. Prokaryotic Cell C. Animal Cell D. Plant Cell E. Yeast Cell 3. The green center structure is called what? A. Cytoplasm B. Large Central Vacuole C. Mitochondria D.

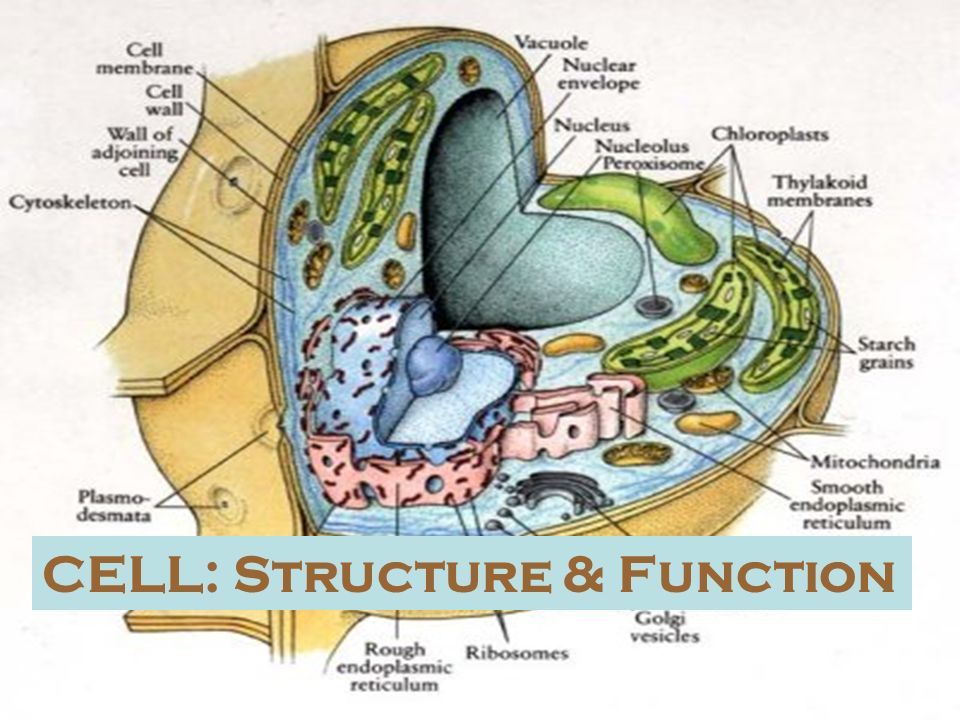
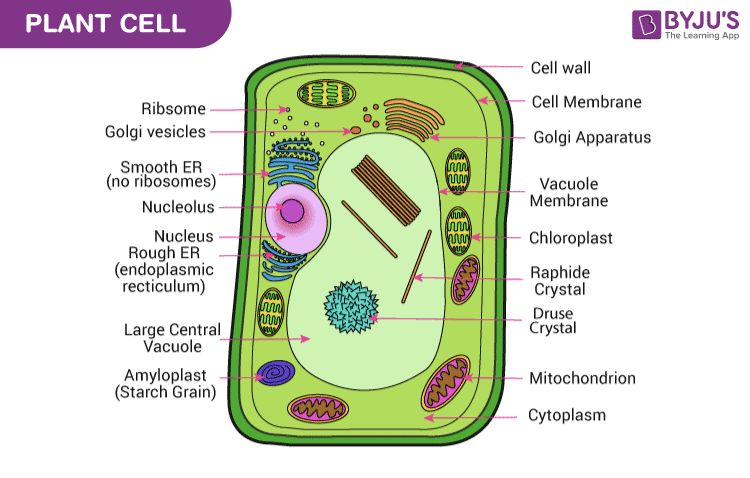
Cell structure with labels
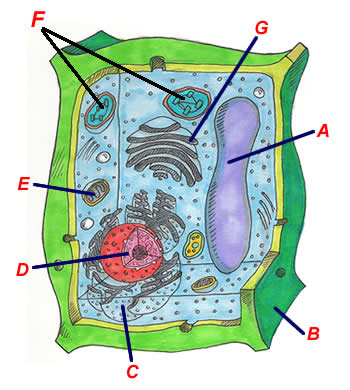
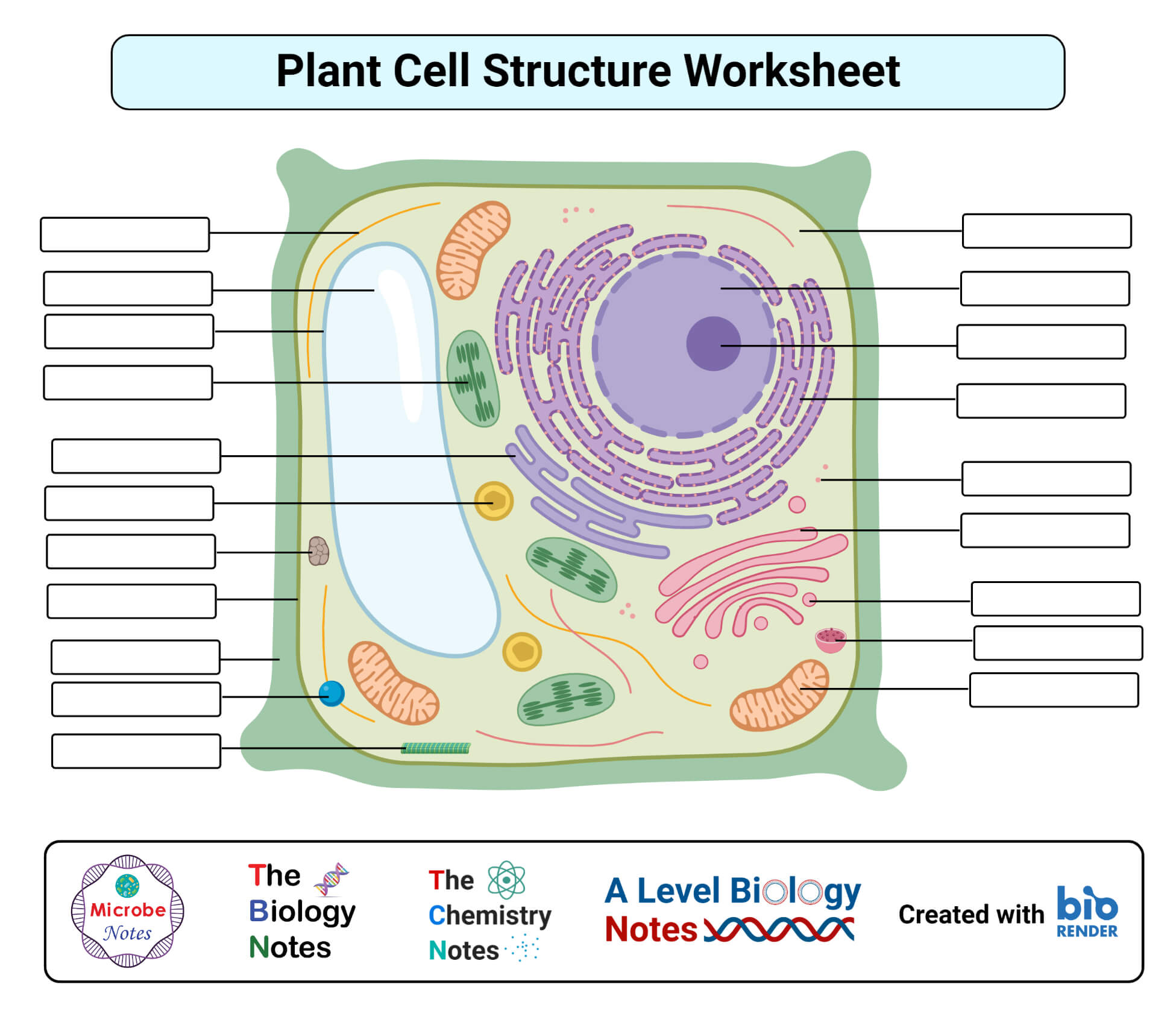
Parts of a Plant Cell - KymanianceEverett The outermost layer is called the cell wall and is unique to plant cells. Store the substances that the cell will. Structure Of A Plant Cell A Visual Guide Plant Cell Plant Cell Structure Plant And Animal Cells There are similarities in the formation of the plant and animal.. They differ in size shape and function. Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) - Genome.gov The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell. Narration 00:00 …
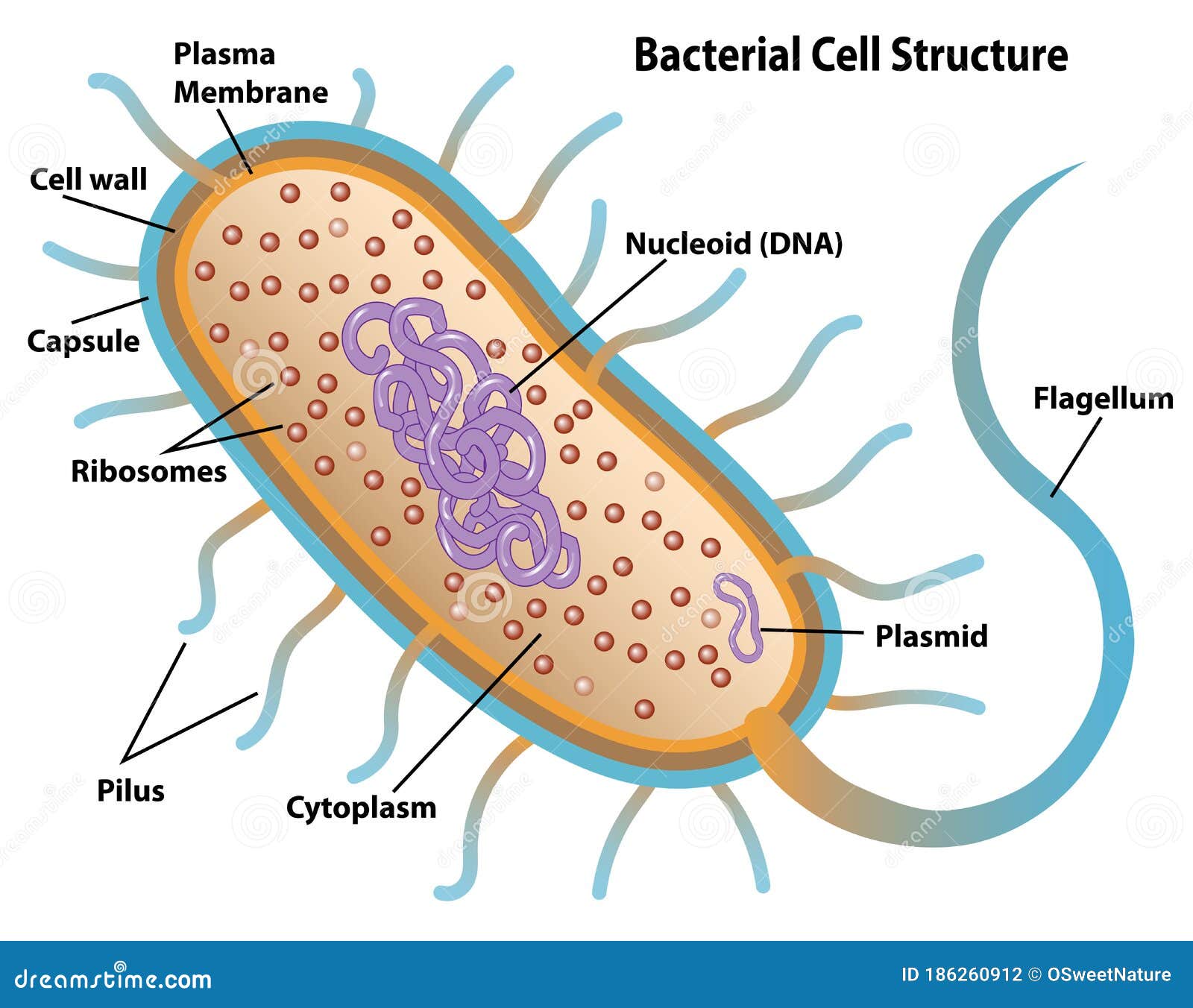
Cell structure with labels. Plant Cell Under Microscope - BrodyanceHenry Cell structure Hydrilla view of the leaf surface showing plant cells under the microscope. Cross section - xylem is a type of tissue in vascular. Browse 196 plant cell under microscope stock photos and images available or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. In a neutral or slightly. Flagella: Structure, Arrangement, Function - Microbe Online Flagella (singular, flagellum) are the locomotory structures of many prokaryotes. Most protozoa and some bacteria are motile. Protozoa use flagella, cilia, or pseudopods, whereas motile bacteria move only using flagella. The flagellum functions by rotation to push or pull the cell through a liquid medium. The cell: Types, functions, and organelles - Medical News Today The cytoplasm is the interior of the cell that surrounds the nucleus. It includes the organelles and a jelly-like fluid called the cytosol. Many of the important reactions that take place in the... Human Biology Lab Online | Lab 4 Tissues and Skin When viewing the slides, please follow these steps: Start on the lowest magnification 40x Move to the next higher magnification 100x View the tissue at 400x (Make your sketch of the tissue at this mag.) Can you identify any of the cell structures Select the Labels "On" button Use the slider bars on the side and bottom to scan around the slide.
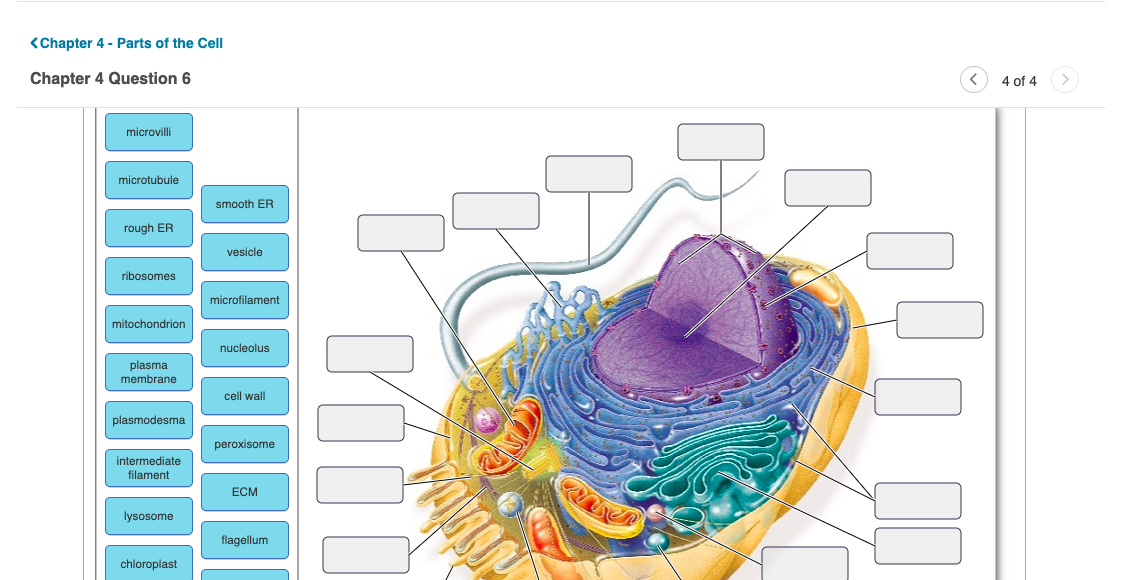
Neuron - Basic Structure and Functions | GetBodySmart Neurons (nerve cells) are the functional units of the nervous system. Even though they vary in size and shape, most have structural characteristics similar to the spinal cord neuron shown to left. Neurons have at their core an expanded area of cytoplasm called the cell body (soma or perikaryon). 1. 2. How to Create 3D Plant Cell and Animal Cell Models for ... - Owlcation Toothpicks and stickers make great labels, and they let everyone know what's what on your cell model. A Deeper Understanding Building a cell model should deepen your understanding of the cell and all of its distinct parts. It's also important to understand the functions of each part and how they work together. Let's take a closer look: Microscopy technique reveals hidden nanostructures in cells and tissues ... Researchers developed a way to 'de-crowd' molecules in a cell by expanding a tissue sample, labeling the molecules, then imaging them. The method, known as expansion revealing, builds on a ... Ultrastructure of cells quiz 1.2 - Subscription websites for IB ... A. Plasma membrane, ribosomes and rER (rough endoplasmic reticulum) B. Cell wall, plasma membrane, ribosomes C. Cell wall, lysosomes, nucleoid region. D. Cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus Check 10 The electron microscope image below shows a cell. What are the organelles shown by the labels A & C? A. A is the cell wall and C is the nucleus. B.
Microscopic Morphology - BIO 2410: Microbiology - Baker College Structure 1 1. What bacterial structure appears as halos around the bacteria show here? 2. What staining procedure was used to prepare this specimen? Structure 1A Structure 2 What bacterial structure can be seen at the label 1? What stain was used to stain these bacteria? Structure 2A Structure 3 What bacterial structure is labeled in this image? Largest Cell in Human Body - JalenmcyPaul Cell Structure Explained There Are Around 75 Trillion Cells In The Human Body But What Are They And How Do They W Cell Structure Organelles Cell Membrane Pin Em Health Facts Desimd Share. No comments for "Largest Cell in Human Body" ... Labels Anak Ask Ayat Berkenaan Best Birthday Biskut Body Bonsai Buat Cara Cell Challange Contoh Darwin Day ... Lac operon- Definition, structure, Inducers, diagram - Microbe Notes The lactose or lac operon of Escherichia coli is a cluster of three structural genes encoding proteins involved in lactose metabolism and the sites on the DNA involved in the regulation of the operon. Many protein -coding genes in bacteria are clustered together in operons which serve as transcriptional units that are coordinately regulated. Diatom - Wikipedia Diatom (Neo-Latin diatoma) refers to any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world.Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from ...
Stratified cuboidal epithelium- structure, functions, examples Structure of stratified cuboidal epithelium The stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of many layers of cells, of which the cells on the outmost layer are cube-shaped. The lower, deeper layers can be both cuboidal or columnar in shape. The cells are tightly packed to ensure no gap is present in two cells.
Researchers find the cell cortex is activated by thousands of short ... One component of the cell is especially important during this process: the cell cortex. This fine network of hair-like filament structures (called actin) just below the cell membrane is the main...
Diagram of Human Heart and Blood Circulation in It A heart diagram labeled will provide plenty of information about the structure of your heart, including the wall of your heart. The wall of the heart has three different layers, such as the Myocardium, the Epicardium, and the Endocardium. Here's more about these three layers. Epicardium
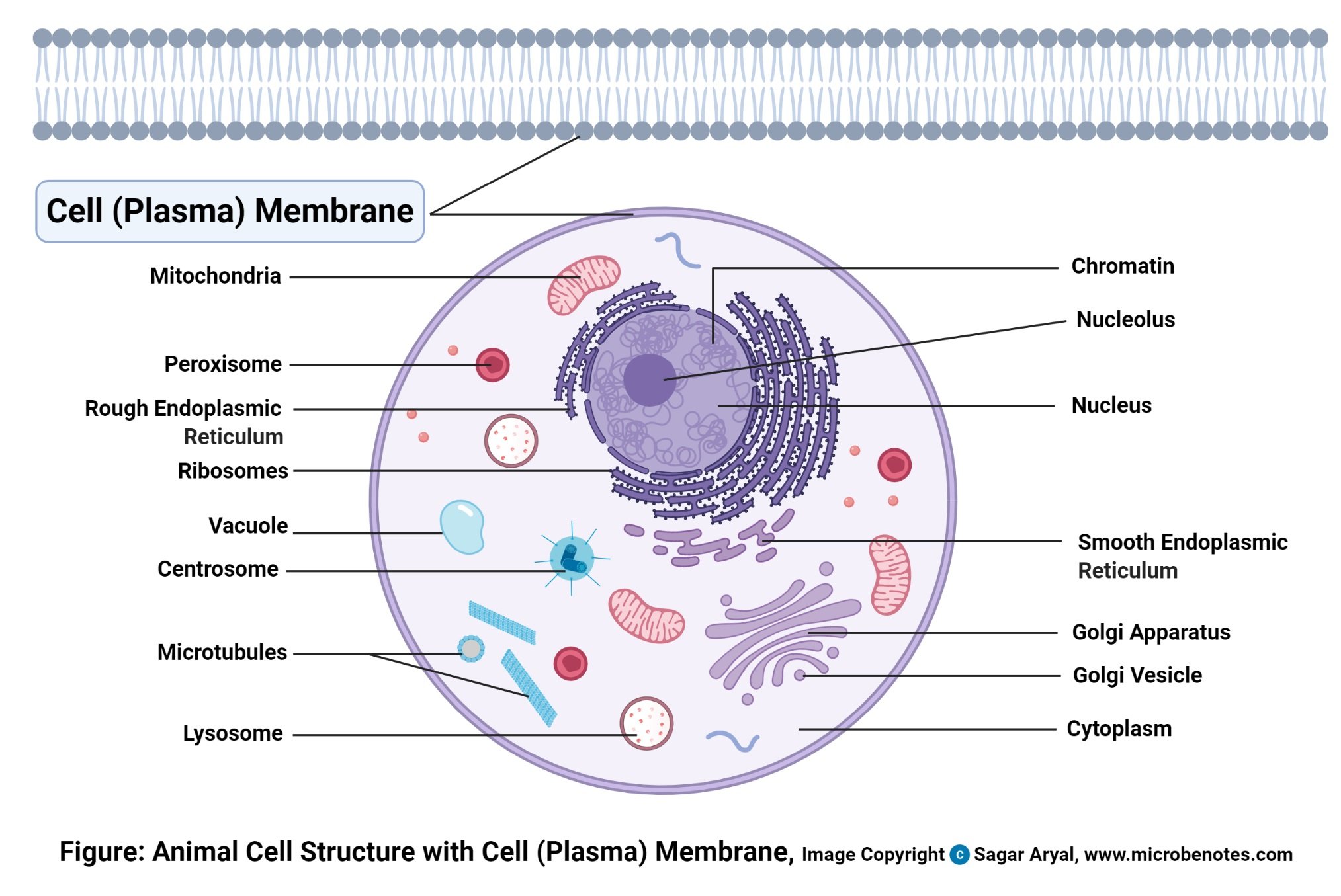
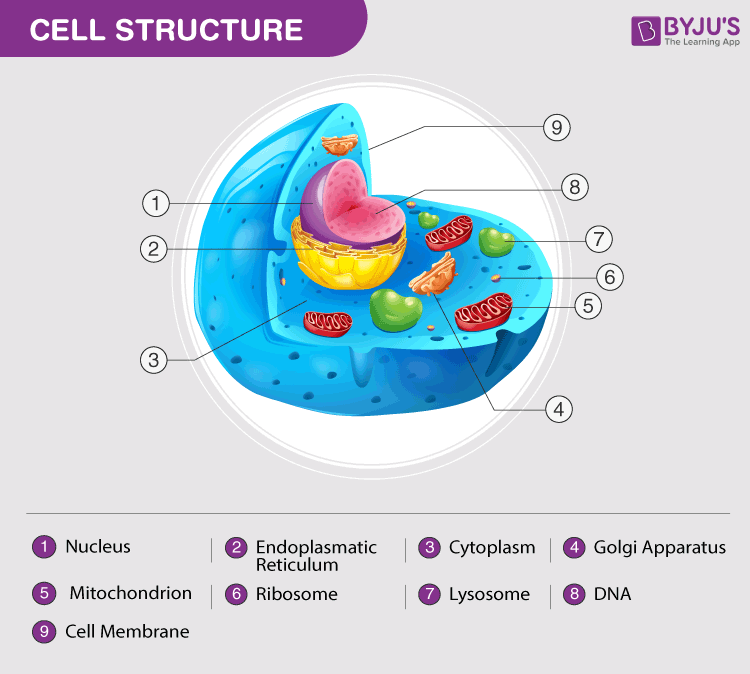
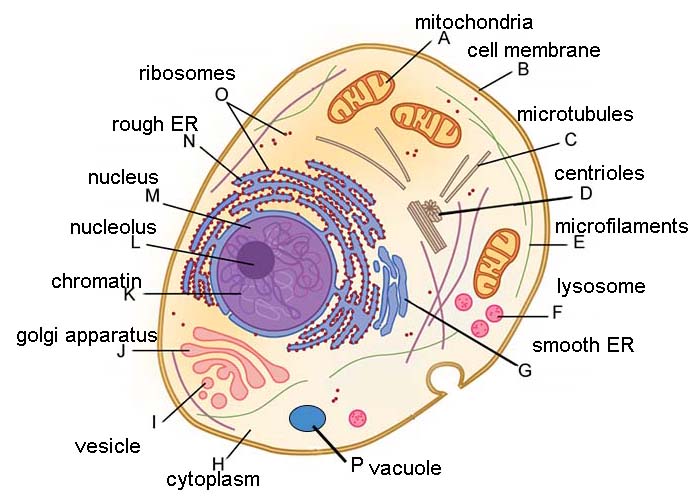
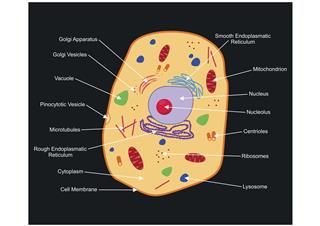
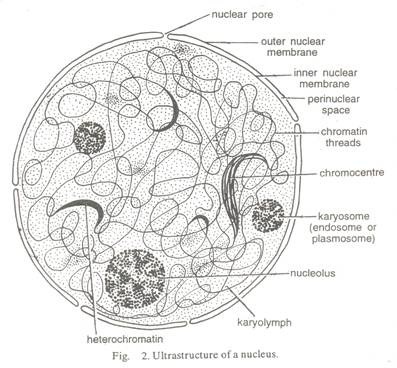
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes Two major regions can be found in a cell. The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles | Kenhub The microfilaments and microtubules are a part of the cellular architecture that helps give the cell its structure ( cytoskeleton) and play a role in cell replication. They also contribute to the formation of cilia and flagella in some cell lines that require motility. Cytoplasm Cytoplasma 1/6 Ribosomes
General Anatomy and Physiology of a Human: TEAS - Registered nursing Anatomy: The study of the parts and structures of the human body. Physiology: The study of the functions of the human body. Gross anatomy: The study of the parts and structures of the human body that can be seen with the naked eye and without the use of a microscope. Microscopic anatomy: The study of the parts and structures of the human body ...
Which cell organelles are present in both animal and plant cells? The plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and contain well developed cellular organelles. The cell membrane, cytoplasm, chromosomes, and mitochondria are the structures that are present in both the plant and the animal cells. The cell wall and chloroplast are present only in the plant cell. Thus, the correct answer is option B.
Membrane Lipids - Microbe Notes Membrane lipids are lipids involved in forming the structure of biological membranes - both the cell membrane and intracellular membranes - and in membrane function, namely compartmentalization of biological processes. Membrane lipids consist primarily of phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol, which can be arranged in bilayers and ...
Stratified columnar epithelium- structure, functions, examples The stratified columnar epithelium consists of many layers of cells, where the cells in the deeper layers are irregular and of different shapes. In contrast, the cells in the apical layer are column-like in shape. The cells in the stratified columnar epithelium, as in the case of simple columnar epithelium are taller than they are wide.
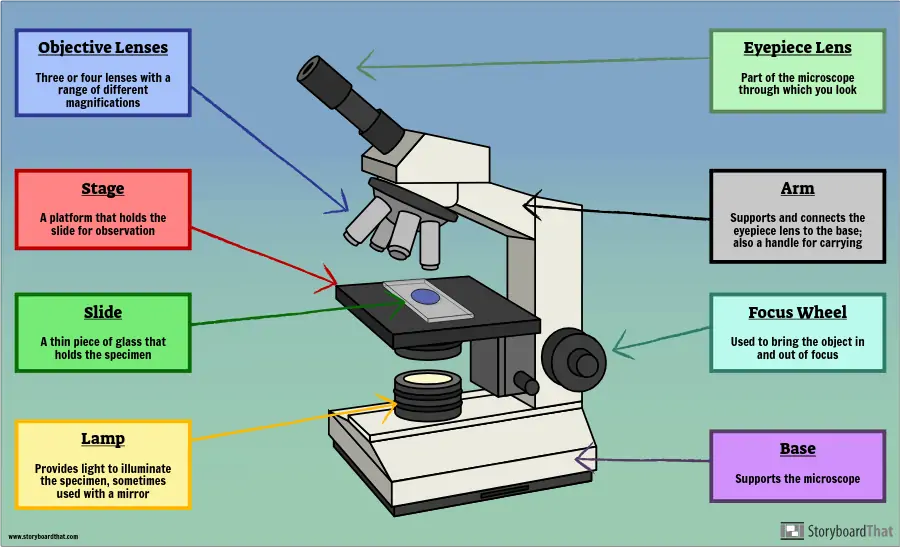
Microscope, Microscope Parts, Labeled Diagram, and Functions Cell staining is a technique used to enhance the visibility of cells and cell components under a microscope. Different stains can be used to stain specific cell components, such as the nucleus or the cell wall, or the entire cell with different colours. What are Basic Components of Optical Microscope?
DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. ...
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) - Genome.gov The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell. Narration 00:00 …
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
Parts of a Plant Cell - KymanianceEverett The outermost layer is called the cell wall and is unique to plant cells. Store the substances that the cell will. Structure Of A Plant Cell A Visual Guide Plant Cell Plant Cell Structure Plant And Animal Cells There are similarities in the formation of the plant and animal.. They differ in size shape and function.























Post a Comment for "45 cell structure with labels"